Diving into the world of Asset allocation strategies, this intro will take you on a journey through the ins and outs of strategic investing. Get ready to explore the key concepts and practical tips that can help you maximize your returns and minimize risks in the investment game.
Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, understanding asset allocation is crucial for building a solid financial future. So, buckle up and let’s navigate the landscape of asset allocation strategies together.
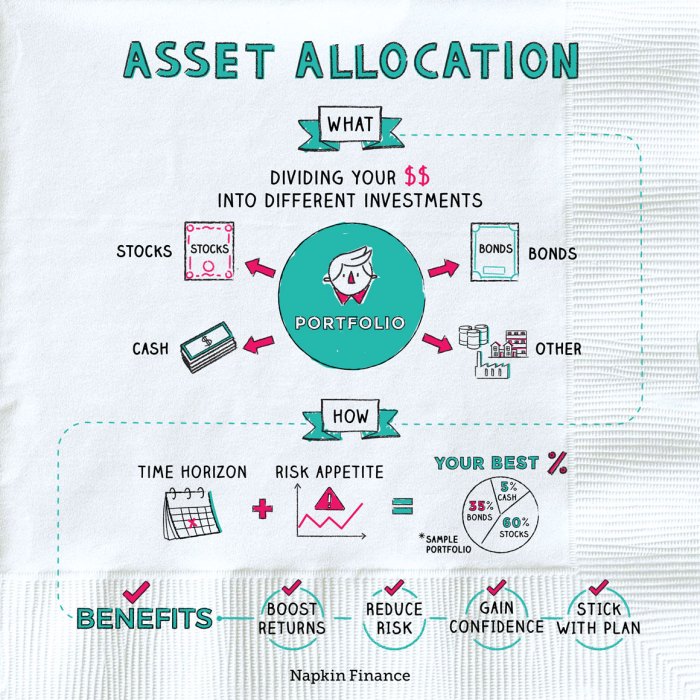
Asset allocation strategies
Asset allocation is the practice of spreading your investments across different asset classes to manage risk and optimize returns.
Different Asset Classes
- Stocks: Represent ownership in a company and offer potential for capital appreciation.
- Bonds: Debt securities issued by governments or corporations providing regular interest payments.
- Real Estate: Includes properties like residential and commercial real estate, offering rental income and potential appreciation.
- Commodities: Raw materials like gold, oil, and agricultural products that can be traded.
Importance of Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is crucial in investment planning as it helps manage risk by diversifying investments across different categories. It also allows investors to take advantage of varying market conditions and achieve a balanced portfolio.
Strategic vs. Tactical Asset Allocation
- Strategic Asset Allocation: Involves setting a target mix of assets based on long-term goals and sticking to it through market fluctuations.
- Tactical Asset Allocation: Involves actively adjusting the asset mix based on short-term market forecasts to capitalize on opportunities or reduce risks.
Traditional Asset Allocation Methods
Asset allocation is a crucial aspect of investment strategy, and traditional methods have been widely used to effectively manage risk and achieve desired returns.
The Principles of Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT) in Asset Allocation
Modern Portfolio Theory, developed by Harry Markowitz, emphasizes diversification to optimize portfolio returns for a given level of risk. MPT assumes that investors are risk-averse and seek to maximize returns while minimizing risk through asset allocation.
Role of Risk Tolerance in Determining Asset Allocation Strategies
Risk tolerance plays a significant role in determining asset allocation strategies. Investors with a higher risk tolerance may allocate more funds to equities for potentially higher returns, while those with lower risk tolerance may lean towards fixed-income investments for stability.
Pros and Cons of Using the Strategic Asset Allocation Method
Strategic asset allocation involves setting target allocations for various asset classes and periodically rebalancing to maintain the desired mix. The pros include long-term focus and disciplined approach, while cons may include missing out on short-term opportunities and potential underperformance during market shifts.
Examples of Traditional Asset Allocation Models such as the 60/40 Portfolio
The 60/40 portfolio is a common traditional asset allocation model where 60% of the portfolio is allocated to equities and 40% to fixed-income securities. This balanced approach aims to achieve growth from equities while providing stability from fixed-income investments.
Alternative asset allocation strategies
When it comes to diversifying your investment portfolio, alternative asset allocation strategies can offer unique opportunities for growth and risk management. These strategies go beyond the traditional methods of investing in stocks and bonds, allowing investors to explore different asset classes and approaches to maximize returns.
Dynamic asset allocation and its benefits
Dynamic asset allocation involves adjusting the allocation of assets in response to changing market conditions. This strategy allows investors to capitalize on market trends and opportunities, potentially enhancing returns and reducing risk. By actively monitoring and reallocating assets based on market dynamics, investors can adapt to changing economic environments and optimize their portfolio performance.
Market timing in asset allocation
Market timing is a strategy where investors attempt to predict the future movements of financial markets to make buy or sell decisions. While market timing can be risky and challenging to execute consistently, some investors believe that it can help capitalize on short-term market fluctuations and generate higher returns. However, market timing requires a deep understanding of market trends and the ability to make accurate predictions, which can be difficult to achieve consistently.
Alternative assets in portfolio diversification
Alternative assets like real estate, commodities, and cryptocurrencies offer unique opportunities for portfolio diversification. By adding these alternative assets to a traditional investment portfolio, investors can reduce overall risk and potentially enhance returns. Real estate provides income through rental properties, commodities offer a hedge against inflation, and cryptocurrencies present opportunities for high growth and diversification beyond traditional markets.
Comparison of alternative asset allocation strategies with traditional methods
- Alternative asset allocation strategies can offer higher returns and lower risk compared to traditional methods due to the diversification benefits of including different asset classes.
- Traditional methods may be more straightforward and easier to implement, but they may not provide the same level of diversification and risk management as alternative strategies.
- Investors should consider their risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon when deciding between traditional and alternative asset allocation strategies to create a well-balanced portfolio.
Rebalancing and monitoring asset allocation
When it comes to managing your investment portfolio, one crucial aspect is regularly rebalancing and monitoring your asset allocation. This ensures that your investments stay aligned with your financial goals and risk tolerance over time.
Importance of Rebalancing
Rebalancing involves realigning your portfolio back to your target asset allocation percentages. This is important because over time, the performance of different asset classes can vary, causing your portfolio to deviate from your original investment plan. By rebalancing, you can maintain the desired level of risk and return in your portfolio.
Guidelines for Rebalancing
- Set a schedule: Decide how often you will rebalance your portfolio, whether it’s quarterly, semi-annually, or annually.
- Thresholds for action: Determine specific percentage thresholds for each asset class that will trigger a rebalance.
- Buy low, sell high: When rebalancing, sell assets that have performed well and buy assets that are underperforming to bring your portfolio back in line with your target allocation.
Role of Periodic Monitoring
Periodic monitoring involves regularly reviewing your portfolio to ensure it remains in line with your goals and risk tolerance. By monitoring your investments, you can identify any deviations from your target allocation and take action accordingly.
Best Practices for Adjusting Asset Allocation
- Stay informed: Keep up to date with market trends and economic conditions that may impact your investments.
- Reassess your goals: Regularly review your financial goals and adjust your asset allocation as needed to reflect any changes in your circumstances.
- Consult with a financial advisor: Seek professional advice to help you make informed decisions about adjusting your asset allocation based on changing market conditions.
