Diving into the realm of Retirement age statistics, we embark on a journey to explore the diverse landscape of retirement ages across the world. From cultural influences to economic factors, we uncover the intriguing patterns that shape retirement decisions globally.
As we delve deeper, we analyze the intricate relationship between retirement age trends and the evolution of social security systems, shedding light on the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Overview of Retirement Age Statistics
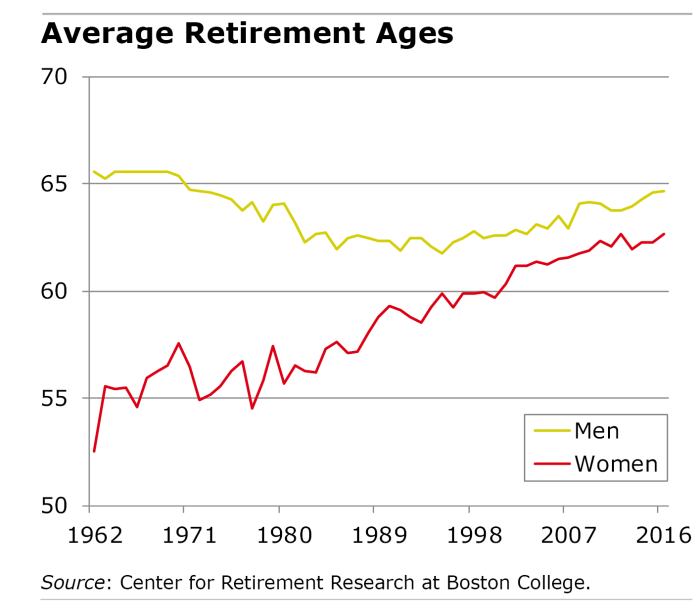
Retirement age is the age at which individuals typically leave the workforce and stop working full-time. It is a significant milestone that varies from country to country, influenced by a variety of factors such as life expectancy, economic conditions, social security systems, and cultural norms. Let’s delve deeper into the retirement age trends around the world.
Factors Influencing Retirement Age Variations Globally
In developed nations, where life expectancy is higher and social security systems are more robust, the retirement age tends to be higher. On the other hand, in developing countries with lower life expectancies and limited social safety nets, the retirement age may be lower. Economic conditions also play a crucial role, with individuals in wealthier countries often working longer to secure their financial stability during retirement.
Comparison of Retirement Age Trends between Developed and Developing Nations
- In developed nations like the United States, the retirement age is gradually increasing due to factors such as rising life expectancy and concerns about the sustainability of pension systems.
- On the contrary, in many developing countries, the retirement age remains relatively low, reflecting the challenges faced by older workers in accessing adequate retirement benefits and healthcare.
- Cultural norms and expectations also impact retirement age variations, with some countries valuing early retirement as a time for leisure and relaxation, while others view continued work as a sign of productivity and contribution to society.
Retirement Age Trends in Different Countries
In today’s globalized world, retirement age trends vary significantly across different countries due to a combination of cultural norms and economic conditions. Let’s take a closer look at how retirement ages compare in countries like the US, Japan, Germany, and Australia.
Comparison of Retirement Ages
In the United States, the full retirement age for Social Security benefits is typically between 66 and 67, depending on the year of birth. Japan has been gradually increasing its retirement age, with the current age set at 65. In Germany, the retirement age is also 65, but there are plans to gradually increase it to 67 by 2031. On the other hand, Australia has a retirement age of 67, which is set to increase to 70 by 2035.
Impact of Cultural Norms and Economic Conditions
Cultural norms play a significant role in determining retirement age decisions. For example, in Japan, there is a strong emphasis on loyalty to one’s employer and a sense of obligation to continue working beyond the traditional retirement age. Economic conditions also influence retirement age, as individuals in countries with robust social security systems may feel more financially secure retiring earlier.
Recent Changes in Retirement Age Policies
Recently, many countries have been facing challenges related to an aging population and increasing life expectancy, prompting discussions about adjusting retirement age policies. For instance, Germany’s decision to gradually raise the retirement age to 67 reflects the need to ensure the sustainability of the pension system in light of demographic changes. Similarly, Australia’s plan to increase the retirement age to 70 by 2035 aims to address the strain on the country’s pension system caused by an aging population.
Gender Disparities in Retirement Age
Gender disparities in retirement age refer to the differences in the age at which men and women typically retire and the implications this has on their financial security and overall well-being. Let’s delve into the statistics and reasons behind these gaps.
Retirement Age Differences Between Men and Women
In many countries, there exists a noticeable gap between the retirement ages of men and women. On average, women tend to retire at a younger age than men. For example, in the United States, the average retirement age for women is 64, while for men it is 66. This discrepancy can have significant consequences for women’s financial stability in their later years.
- Women often earn less than men over their lifetimes due to the gender pay gap, which can result in lower retirement savings.
- Women are more likely to take breaks from the workforce to care for children or elderly relatives, impacting their ability to save for retirement.
- Women tend to live longer than men, meaning they need to stretch their retirement savings over a longer period.
Reasons Behind Gender Disparities in Retirement Age
The gender disparities in retirement age can be attributed to various societal and economic factors that impact men and women differently.
One major factor is the gender pay gap, which results in women earning less over their careers and accumulating less in retirement savings.
- Traditional gender roles often place the responsibility of caregiving on women, leading to career interruptions and lower lifetime earnings.
- Women may have less access to employer-sponsored retirement plans or benefits, further hindering their ability to save for retirement.
- Cultural norms and expectations around retirement age may differ for men and women, influencing their decisions on when to retire.
Impact of Retirement Age on Social Security Systems
The retirement age has a significant impact on the sustainability of social security programs around the world. As people live longer and retire later, governments face challenges in ensuring the financial viability of these programs. Let’s delve deeper into how retirement age affects social security systems.
Challenges Faced by Governments
- Increased Financial Strain: With a higher retirement age, more people are eligible for benefits for a longer period, putting a strain on the financial resources of social security programs.
- Demographic Shifts: Changing retirement age demographics, with a larger proportion of elderly individuals, require adjustments to social security policies to meet the needs of an aging population.
- Political and Social Pressures: Governments may face resistance from citizens when considering raising the retirement age, leading to challenges in implementing necessary reforms.
Effectiveness of Raising Retirement Age
- Addressing Economic Concerns: Raising the retirement age can help mitigate the economic challenges posed by an aging population, ensuring the long-term sustainability of social security systems.
- Encouraging Workforce Participation: By extending the retirement age, governments can encourage older individuals to remain in the workforce, contributing to economic growth and reducing dependency on social security benefits.
- Balancing Act: Governments need to strike a balance between raising the retirement age to address economic concerns and ensuring that older individuals have adequate support and resources during their extended working years.
