As Understanding wealth inequality takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Exploring the complexities of wealth distribution and its impact on society, this discussion delves into the factors, social implications, demographic influences, and proposed solutions related to wealth inequality.
Factors contributing to wealth inequality
Historical events, policies, globalization, and technological advancements have all played significant roles in shaping wealth distribution.
Historical events shaping wealth distribution
Historical events such as colonization, slavery, and discriminatory practices have laid the foundation for wealth inequality. For example, the legacy of slavery in the United States has led to disparities in wealth accumulation between white and Black Americans.
Policies exacerbating or alleviating wealth inequality
Policies like progressive taxation, minimum wage laws, and social welfare programs can help alleviate wealth inequality by redistributing resources. On the other hand, tax cuts for the wealthy, deregulation, and corporate welfare can exacerbate wealth inequality by favoring the rich.
Impact of globalization on wealth distribution
Globalization has contributed to wealth inequality by enabling the flow of capital across borders, allowing multinational corporations to exploit cheap labor in developing countries. This has led to the concentration of wealth in the hands of a few wealthy individuals and corporations.
Technological advancements influencing wealth inequality
Technological advancements have both created opportunities for wealth accumulation and exacerbated inequality. Industries like tech and finance have seen massive wealth creation, but automation and artificial intelligence have also led to job displacement and wage stagnation for many workers, widening the wealth gap.
Social implications of wealth inequality
Wealth inequality has significant social implications that impact various aspects of society, including access to education, healthcare disparities, social mobility, and potential for social unrest.
Access to education
Access to quality education is often limited by wealth inequality. Families with lower income levels may struggle to afford resources such as tutoring, educational materials, or access to extracurricular activities that can enhance a student’s learning experience.
Healthcare disparities
Wealth inequality is closely linked to healthcare disparities, as individuals with lower income levels may not have access to quality healthcare services. This can result in poorer health outcomes and a cycle of poverty perpetuated by limited access to essential medical care.
Social mobility
Wealth inequality can hinder social mobility, making it difficult for individuals from lower-income backgrounds to move up the economic ladder. Limited access to resources and opportunities can create barriers to achieving upward mobility and perpetuate intergenerational poverty.
Social unrest
Wealth inequality can lead to social unrest as disparities in wealth distribution become more pronounced. When a significant portion of the population struggles to meet basic needs while a small minority holds a disproportionate amount of wealth, tensions can rise, leading to protests, riots, and other forms of social upheaval.
Demographic factors influencing wealth distribution
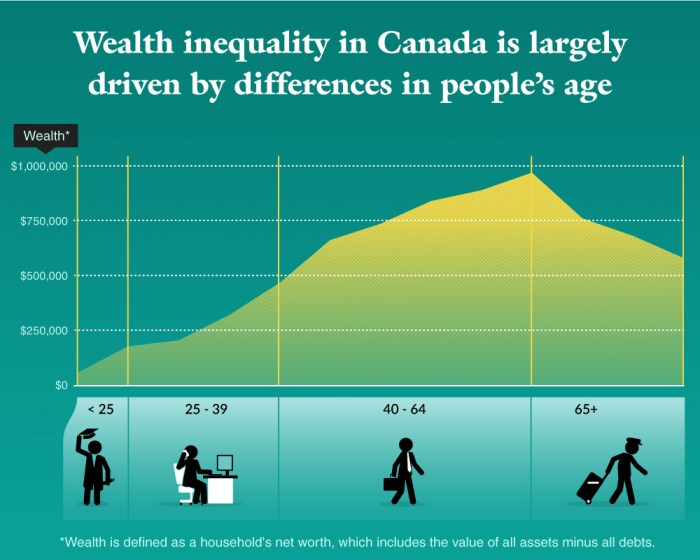
Age demographics, race and ethnicity, gender, and geographical location all play a significant role in wealth distribution. Let’s delve into how these demographic factors impact wealth accumulation.
Age demographics impact on wealth accumulation
Age demographics have a direct impact on wealth accumulation. Younger individuals typically have less wealth due to starting their careers and saving for the future. As individuals age and advance in their careers, they tend to accumulate more wealth through investments, savings, and assets. Older individuals may have more wealth due to years of accumulation and retirement savings.
Role of race and ethnicity in wealth inequality
Race and ethnicity also play a crucial role in wealth inequality. Historical factors, discrimination, and systemic barriers have led to disparities in wealth accumulation among different racial and ethnic groups. For example, Black and Hispanic households tend to have lower wealth compared to White households, highlighting the impact of race on wealth distribution.
Gender wealth gap and its implications
The gender wealth gap refers to the differences in wealth accumulation between men and women. Women often earn less than men, leading to lower savings, investments, and assets. Factors such as pay inequality, caregiving responsibilities, and limited access to financial resources contribute to the gender wealth gap. Closing this gap is essential for promoting financial equality and empowerment among women.
Geographical location affecting wealth distribution
Geographical location can also affect wealth distribution. Individuals living in urban areas with higher costs of living may have less disposable income to save and invest, impacting their wealth accumulation. Additionally, access to economic opportunities, resources, and social services can vary based on location, influencing wealth disparities among different regions.
Solutions to address wealth inequality
Progressive taxation is a key tool in reducing wealth inequality by taxing higher earners at a higher rate. This system aims to redistribute wealth by ensuring that those who can afford to contribute more do so, helping to fund social programs and support for those in need.
Effectiveness of progressive taxation
- Progressive taxation helps generate revenue for social welfare programs that can benefit lower-income individuals and families.
- By taxing the wealthier individuals more, it aims to reduce the wealth gap and promote a more equitable distribution of resources.
- However, the effectiveness of progressive taxation depends on proper implementation and enforcement to prevent tax evasion.
Impact of education and skill development programs
- Education and skill development programs play a crucial role in wealth distribution by providing individuals with the tools and knowledge to access higher-paying jobs.
- Investing in education can help individuals break the cycle of poverty and increase their earning potential, ultimately narrowing the wealth gap.
- Access to quality education for all socio-economic backgrounds is essential in promoting equal opportunities for wealth accumulation.
Access to affordable housing
- Access to affordable housing can help narrow the wealth gap by providing individuals with stable living conditions and reducing the financial burden of housing expenses.
- Affordable housing initiatives can prevent homelessness and enable individuals to save and invest in other areas, contributing to wealth accumulation.
- Policies that promote affordable housing options for low-income individuals are essential in addressing wealth inequality.
Role of financial literacy
- Financial literacy plays a crucial role in addressing wealth inequality by empowering individuals to make informed financial decisions and manage their resources effectively.
- By increasing financial literacy, individuals can better understand the importance of saving, investing, and managing debt, leading to improved wealth accumulation.
- Efforts to promote financial education and provide resources for individuals to improve their financial skills are essential in reducing wealth inequality.
