Diving deep into the world of Retirement planning for self-employed, this intro sets the stage for an exciting exploration of financial independence and future security. Get ready to discover the ins and outs of retirement savings strategies that can empower you to take control of your financial future.
In the following paragraphs, we’ll break down the importance of retirement planning, explore various savings options, delve into tax considerations, and tackle challenges faced by self-employed individuals.
Importance of Retirement Planning for Self-Employed Individuals
Retirement planning is crucial for self-employed individuals as it ensures financial security and stability during their retirement years. Unlike employees who may have access to retirement benefits through their employers, self-employed individuals are responsible for creating their own retirement savings plan.
Differences in Retirement Planning
Self-employed individuals need to be more proactive in planning for retirement compared to traditional employees. They have to set up their own retirement accounts, such as a SEP IRA or Solo 401(k), and contribute to them regularly. Additionally, they do not benefit from employer contributions or matching funds, making it even more essential to save consistently.
Impact of Lack of Retirement Planning
Without proper retirement planning, self-employed individuals may face financial struggles in their later years. They risk not having enough savings to maintain their lifestyle or cover medical expenses. This can lead to a significant decrease in their quality of life during retirement. It is essential for self-employed individuals to prioritize retirement planning to secure their financial future.
Retirement Savings Options for Self-Employed Individuals
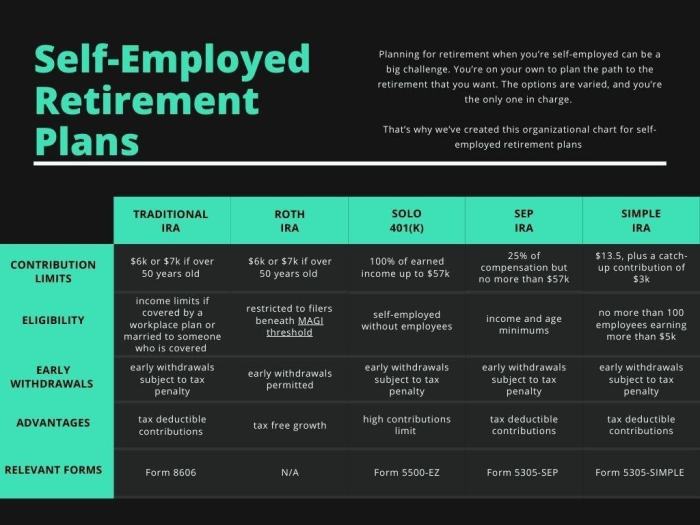
When it comes to retirement savings, self-employed individuals have several options to choose from to secure their financial future. Let’s explore the various retirement savings options available and how they compare to help you make an informed decision.
SEP-IRA
A Simplified Employee Pension Individual Retirement Account (SEP-IRA) allows self-employed individuals to contribute up to 25% of their net earnings, up to a maximum annual limit. Contributions are tax-deductible and grow tax-deferred until withdrawal. This option is ideal for small business owners with fluctuating income.
Solo 401(k)
A Solo 401(k) plan is designed for self-employed individuals with no employees other than a spouse. It enables contributions as both the employer and employee, allowing for higher contribution limits compared to a SEP-IRA. This option provides flexibility in investment choices and potential for tax-free loans.
SIMPLE IRA
A Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees (SIMPLE) IRA is a retirement plan for small businesses with fewer than 100 employees. It offers both employer and employee contributions, with lower contribution limits than a Solo 401(k) but simpler administrative requirements. This option is suitable for self-employed individuals looking for a straightforward retirement savings plan.
By comparing the features of each retirement savings option, self-employed individuals can assess their needs and choose the most suitable option based on factors like income level, business structure, and retirement goals. It’s essential to consider factors such as contribution limits, tax advantages, investment flexibility, and administrative requirements to make an informed decision that aligns with your financial objectives.
Tax Considerations in Retirement Planning for Self-Employed Individuals
When it comes to retirement planning for self-employed individuals, understanding the tax implications is crucial. Proper planning can help reduce tax liabilities and maximize savings for the future.
Tax Advantages of Retirement Savings Options
- One of the key tax advantages for self-employed individuals is the ability to contribute to tax-deferred retirement accounts, such as a SEP-IRA or Solo 401(k). These contributions are typically tax-deductible, reducing taxable income for the year.
- Self-employed individuals can also take advantage of catch-up contributions if they are over the age of 50, allowing them to contribute additional funds to their retirement accounts and further reduce tax liabilities.
- Contributions to Roth retirement accounts, like a Roth IRA or Roth Solo 401(k), are made with after-tax dollars but offer tax-free growth and withdrawals in retirement, providing tax diversification for future tax planning.
Strategies for Maximizing Tax Benefits
- Consider consulting with a tax professional or financial advisor to determine the most tax-efficient retirement savings options based on your individual circumstances and goals.
- Regularly review and adjust your retirement plan to take advantage of any changes in tax laws or regulations that could impact your tax liabilities and retirement savings.
- Explore additional tax planning strategies, such as income deferral or income shifting, to optimize your tax situation while saving for retirement as a self-employed individual.
Challenges and Solutions in Retirement Planning for Self-Employed Individuals
When it comes to retirement planning, self-employed individuals face unique challenges that can make saving for the future more difficult. From fluctuating income to market volatility, there are several obstacles that can hinder effective retirement planning. However, with the right strategies in place, self-employed individuals can overcome these challenges and secure their financial future.
Common Challenges Faced by Self-Employed Individuals
- Fluctuating Income: Self-employed individuals often have irregular income streams, making it challenging to set aside a consistent amount for retirement savings.
- Lack of Employer-sponsored Retirement Plans: Unlike employees who have access to 401(k) or pension plans, self-employed individuals must find alternative retirement savings options.
- Market Volatility: The unpredictable nature of the stock market can make it difficult for self-employed individuals to grow their retirement savings consistently.
Solutions to Overcome These Challenges
- Set a Budget and Stick to It: Creating a budget can help self-employed individuals manage their fluctuating income and allocate a certain percentage towards retirement savings each month.
- Explore Retirement Account Options: Self-employed individuals can consider setting up a Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA or a Solo 401(k) to save for retirement and take advantage of tax benefits.
- Diversify Investments: To mitigate the impact of market volatility, self-employed individuals can diversify their investment portfolio across different asset classes.
Creating a Retirement Planning Strategy
- Consult with a Financial Advisor: Seeking guidance from a financial advisor can help self-employed individuals create a personalized retirement planning strategy that aligns with their goals and risk tolerance.
- Regularly Review and Adjust: It’s essential for self-employed individuals to regularly review their retirement savings strategy and make adjustments as needed based on changes in income, expenses, and market conditions.
- Plan for Uncertainties: Building an emergency fund and having a contingency plan in place can help self-employed individuals navigate unexpected financial challenges during retirement.
