When it comes to borrowing money, the choice between secured and unsecured loans can have a significant impact on your financial future. Secured loans are backed by collateral, while unsecured loans are not, leading to various implications in terms of risk, interest rates, and eligibility criteria. Let’s dive into the world of secured vs. unsecured loans to unravel their distinct characteristics and help you make informed decisions.
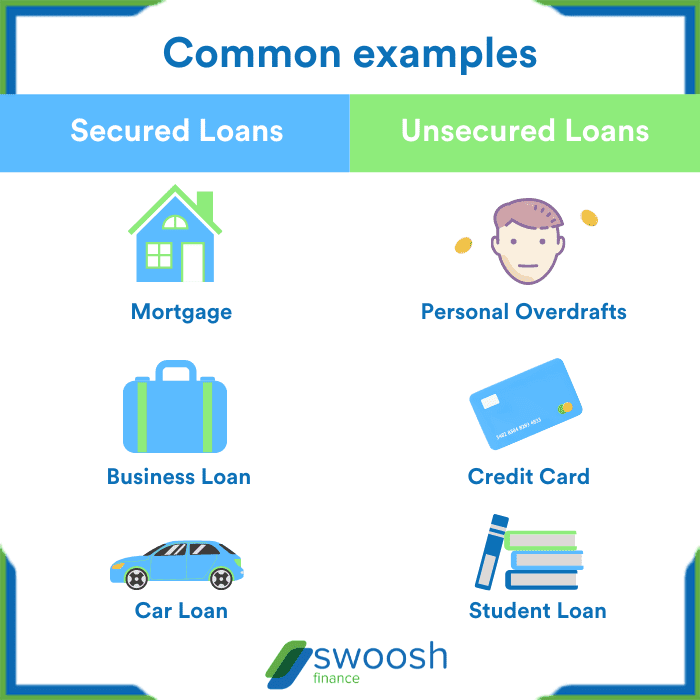
Secured vs. unsecured loans
When it comes to securing that bag, loans play a key role in helping you out. Let’s break down the key differences between secured and unsecured loans.
Secured Loans
Secured loans are like having a backup plan – you put up collateral to protect the lender in case you can’t pay back the loan. This collateral could be your car, house, or any valuable asset. Because of this security, lenders are more willing to offer larger amounts and lower interest rates.
Unsecured Loans
On the flip side, unsecured loans don’t require any collateral. It’s like borrowing money based on your promise to repay. Since there’s no security for the lender, unsecured loans usually come with higher interest rates and lower borrowing limits.
Collateral Impact
Collateral in secured loans acts as a safety net for lenders, giving them assurance that they can recover their money if you default. This security allows borrowers to access larger loan amounts and better interest rates. However, failing to repay a secured loan can lead to losing the pledged collateral.
Risks
Secured loans pose a greater risk to borrowers as they risk losing their assets if they can’t make payments. On the other hand, unsecured loans carry the risk of damaging your credit score if you default, leading to higher interest rates in the future.
Interest Rates
Interest rates for secured loans are generally lower than unsecured loans due to the reduced risk for lenders. This means you could end up paying less in interest over the life of the loan with a secured option.
Collateral in secured loans
When it comes to secured loans, collateral plays a crucial role in the borrowing process. Collateral is an asset that a borrower pledges to a lender to secure a loan, reducing the risk for the lender in case the borrower defaults. Let’s dive into the types of assets commonly used as collateral, situations where collateral may be required, the process of valuing collateral, and the consequences of defaulting on a secured loan related to collateral.
Types of assets commonly used as collateral
Collateral for secured loans can vary, but some common types of assets include real estate (such as a house or land), vehicles (like cars or boats), investments (stocks or bonds), and valuable personal property (jewelry or art).
Examples of situations where collateral may be required
Collateral may be required when borrowing a large sum of money, starting a new business, purchasing a home or a car, or if the borrower has a low credit score. Lenders often ask for collateral to mitigate the risk of lending to individuals with a higher chance of defaulting.
Valuing collateral and its impact on loan approval
The process of valuing collateral involves assessing the market value of the asset and determining its potential worth in case of default. Lenders may require an appraisal or inspection to establish the value of the collateral. The value of the collateral can directly impact the loan amount approved, interest rates, and repayment terms.
Consequences of defaulting on a secured loan
If a borrower defaults on a secured loan, the lender has the right to seize and sell the collateral to recover the outstanding debt. This can result in the loss of the asset used as collateral and damage the borrower’s credit score. Defaulting on a secured loan can have long-term financial implications and make it harder to secure credit in the future.
Eligibility and application process
When it comes to securing a loan, whether it’s secured or unsecured, there are specific eligibility criteria and application processes that borrowers need to be aware of. Let’s dive into the details of what it takes to qualify for these types of loans and what documentation is required during the application process.
Eligibility Criteria
- Secured Loans: Typically, eligibility for secured loans is based on the value of the collateral provided by the borrower. Lenders may also consider the borrower’s credit score, income, and debt-to-income ratio.
- Unsecured Loans: Eligibility for unsecured loans is primarily based on the borrower’s creditworthiness. Lenders will assess the borrower’s credit score, income stability, and employment status.
Documentation Required
- Secured Loans: When applying for a secured loan, borrowers will need to provide documentation related to the collateral being used, such as property deeds, vehicle titles, or savings account statements.
- Unsecured Loans: For unsecured loans, borrowers typically need to submit proof of income, bank statements, and identification documents, such as a driver’s license or passport.
Approval Process and Timeframes
- Secured Loans: The approval process for secured loans may take longer due to the need for the lender to appraise the collateral. Once all documentation is submitted, approval can take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks.
- Unsecured Loans: Approval for unsecured loans is generally quicker since there is no collateral involved. Borrowers with good credit may receive approval within a day or two, while those with lower credit scores may face a longer approval process.
Application Fees
- Secured Loans: Since secured loans involve more extensive documentation and appraisal processes, borrowers may incur higher application fees to cover these costs.
- Unsecured Loans: Application fees for unsecured loans are typically lower compared to secured loans, as there is less risk involved for the lender.
Flexibility and Repayment Terms
When it comes to flexibility and repayment terms, secured and unsecured loans have distinct differences that borrowers need to consider. Let’s delve into how these factors play out in each type of loan.
Flexibility in Secured Loans
Secured loans typically offer more flexibility in terms of loan amount and repayment schedules due to the presence of collateral. Lenders are more willing to provide higher loan amounts and longer repayment periods because the collateral reduces their risk. Borrowers can negotiate the terms based on the value of the collateral, allowing for more customized loan options.
Impact of Collateral in Unsecured Loans
In contrast, unsecured loans do not require collateral, which can impact the repayment terms. Lenders may be more cautious in offering larger loan amounts and longer repayment periods since there is no asset securing the loan. This can result in higher interest rates and stricter repayment schedules to mitigate the risk for the lender.
Repayment Period Comparison
Secured loans often offer longer repayment periods compared to unsecured loans. For example, a mortgage, which is a type of secured loan, can have repayment terms of 15 to 30 years. On the other hand, unsecured personal loans typically have shorter repayment periods ranging from a few months to 5 years. The longer repayment period in secured loans can make monthly payments more manageable for borrowers.
Options in Financial Difficulties
In case of financial difficulties when repaying a secured loan, borrowers may have the option to renegotiate the terms with the lender. This could involve extending the repayment period, modifying the interest rate, or finding other solutions to ensure timely repayment. For unsecured loans, borrowers may need to explore debt consolidation, debt settlement, or other financial assistance options to manage repayment challenges effectively.
