Dive into the world of stock options where financial opportunities abound and risks lurk around every corner. Understanding stock options opens up a realm of possibilities for investors seeking to navigate the complex landscape of the stock market.
From the basics of stock options to the intricate details of call and put options, this exploration will equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions in the fast-paced world of trading.
Introduction to Stock Options
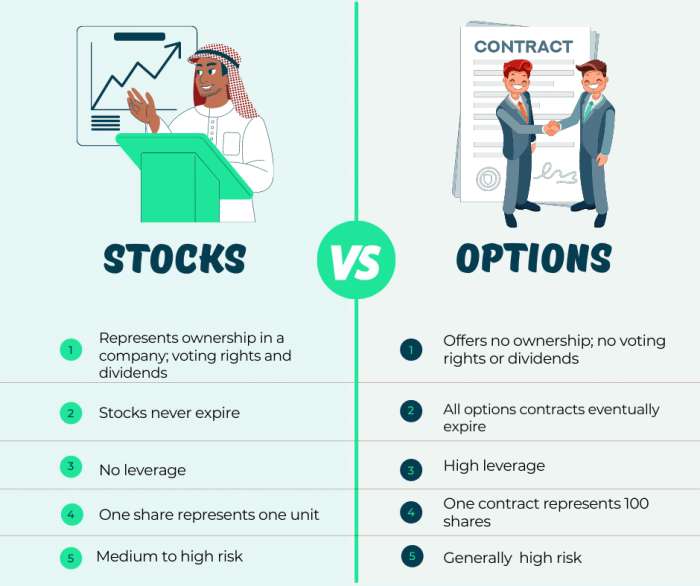
Stock options are financial instruments that give the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a specific amount of stock at a predetermined price within a set timeframe. They are commonly used as a form of compensation for employees or as investment vehicles for traders.
Types of Stock Options
- 1. Call Options: These give the holder the right to buy a specific amount of stock at a predetermined price, known as the strike price, before the expiration date.
- 2. Put Options: These give the holder the right to sell a specific amount of stock at a predetermined price before the expiration date.
Importance of Stock Options
Stock options play a crucial role in the financial market by providing investors with opportunities to speculate on the movement of stock prices without actually owning the underlying assets. They also serve as a way for companies to attract and retain talent by offering employees a stake in the company’s performance through stock option grants.
Understanding Call and Put Options
When it comes to stock options, investors often have the choice between call options and put options. These two types of options provide different opportunities for investors to either profit or protect their investments.
Call Options
Call options give investors the right, but not the obligation, to buy a specific amount of a stock at a predetermined price within a specified time frame. Investors typically use call options when they believe the price of the underlying stock will rise, allowing them to purchase the stock at a lower price than what it may be trading for in the future.
- Investors can profit from call options by buying the options at a lower price and then selling them at a higher price if the stock price increases.
- Call options can also be used as a way to hedge against potential losses in a stock position.
- It’s important to note that investors must pay a premium to purchase call options, which represents the cost of acquiring the right to buy the stock at a specific price.
Put Options
Put options, on the other hand, give investors the right, but not the obligation, to sell a specific amount of a stock at a predetermined price within a specified time frame. Investors typically use put options when they believe the price of the underlying stock will decrease, allowing them to sell the stock at a higher price than what it may be trading for in the future.
- Investors can profit from put options by selling the options at a higher price if the stock price decreases below the predetermined price.
- Put options can also be used as a way to protect gains in a stock position or to speculate on a stock’s decline.
- Similar to call options, investors must pay a premium to purchase put options, which represents the cost of acquiring the right to sell the stock at a specific price.
Factors Influencing Option Prices
When it comes to stock options, there are several key factors that influence their pricing. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions in the options market.
Volatility, time to expiration, and the underlying asset price are the main factors that affect option prices. Let’s break down how each of these factors plays a role in determining the value of an option.
Volatility
Volatility refers to the degree of variation in the price of the underlying asset. Higher volatility generally leads to higher option premiums, as there is a greater likelihood of large price swings. On the other hand, lower volatility tends to result in lower option prices. For example, if a stock is known for its volatile price movements, the options on that stock will likely be more expensive compared to options on a stable stock.
Time to Expiration
The amount of time until an option expires is another crucial factor in determining its price. As the expiration date approaches, the time value of the option decreases. This is because the probability of the option ending in-the-money diminishes as time passes. Therefore, options with longer expiration periods will have higher premiums compared to options with shorter expiration periods. For instance, a call option with three months until expiration will be priced higher than the same call option with only one month until expiration.
Underlying Asset Price
The price of the underlying asset also plays a significant role in option pricing. For call options, as the price of the underlying asset increases, the value of the call option also increases. Conversely, for put options, as the price of the underlying asset goes up, the value of the put option decreases. For example, if you hold a call option on a stock and the stock price rises, the value of your call option will also increase.
These factors interact with each other to determine the price of an option, making options pricing a complex and dynamic process in the financial markets.
Risks and Benefits of Trading Stock Options
When it comes to trading stock options, there are both risks and benefits that investors need to consider. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions in the market.
Risks of Trading Stock Options
- Market Volatility: Stock options are highly sensitive to market changes, and sudden fluctuations can lead to significant losses.
- Time Decay: Options have an expiration date, and as time passes, the value of the option may decrease, leading to potential loss for the trader.
- Leverage: Options allow traders to control a large amount of stock with a small investment. While this can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses.
- Lack of Liquidity: Some options may have low trading volume, making it difficult to buy or sell them at desired prices.
Benefits of Trading Stock Options
- Diversification: Options provide an opportunity to diversify an investment portfolio and hedge against market risks.
- Potential for Higher Returns: Options offer the potential for high returns compared to traditional stock trading, especially in volatile markets.
- Risk Management: Options can be used to protect against downside risk or limit potential losses in a stock position.
- Flexibility: Options offer a variety of strategies that can be tailored to different market conditions and investment goals.
Real-World Examples of Option Trading
- Successful Scenario: An investor purchases call options on a tech stock before a positive earnings report, leading to a significant profit as the stock price rises.
- Unsuccessful Scenario: A trader fails to set a stop-loss order on a put option, resulting in substantial losses when the stock price unexpectedly rebounds.
